Description- Filling in gaps to create a complete, whole object.
Example -
Continuity
Description- Perceiving smooth, continuous patterns rather than discontinuous ones.
Example -
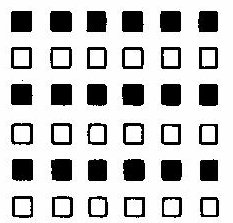
Similarity
Description- Grouping together figures that are similar to each other.
Example -
Proximity
Description- Grouping nearby figures together.
Example-
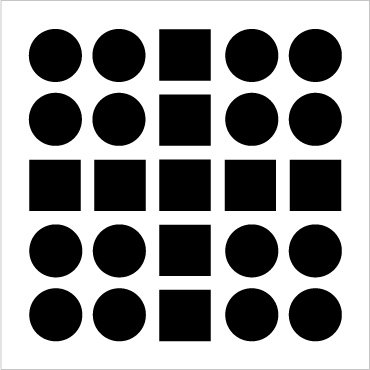
Figure-Ground
Description- relationship continually reverses, but always we organize the stimulus into a figure seen against a ground
Example-

A Binocular Cue
Description- Depth cues, such as retinal disparity and convergence, that depend on the use of two eyes; judging the distance of two object
Example-

Monocular Cues
Texture Gradient
Description- A gradual change from a coarse, distinct texture to a fine, indistinct texture signals increasing distance. Objects far away appear smaller and more densely packed.
Example-
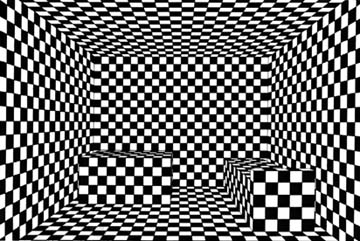
Linear Perspective
Description- Parallel lines, such as railroad tracks appear to converge with distance. The more the lines converge, the greater their perceived distance.
Example-
Motion Perception
Description- Large objects appear to move more slowly than smaller objects
Example- When a truck and car are driving and the truck appears to be moving slower than the cars.
Size Constancy
Description- Perceiving objects having constant size while the distance varies
Example-
Brightness Constancy
Description- Also called lightness constancy, perceiving an object as having a constant lightness even while its illumination varies.
Example-
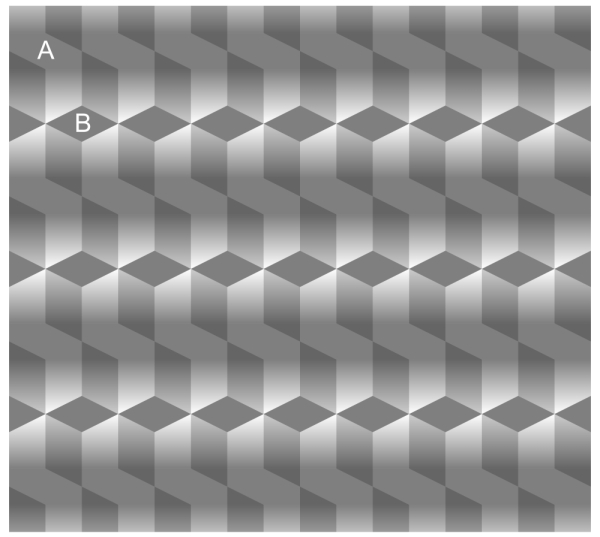
Shape Constancy
Description- Perceiving the form of familiar objects as constant even while our retinal images of them change.
Example-
